
How to Create Login, User and Grant Permissions in SQL Server
How to Create New Login in SQL Server
Here is how to create login in SQL Server:
Step 1) To create login SQL server, Navigate to Security > Logins
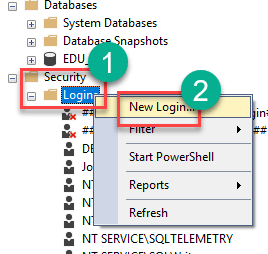
Step 2) In the next screen, Enter
- Login Name
- Select SQL Server authentication
- Enter Password for MySQL create user with password
- Click Ok

Step 3) Login is created
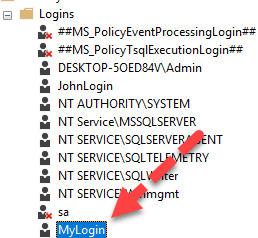
You can also create a login using the T-SQL command for SQL server create login and user.
CREATE LOGIN MyLogin WITH PASSWORD = '123';
How to Create a User in SQL Server Database
A user is an account that you can use to access the SQL server. To create user SQL server, you can use any of the following two ways:
- Using T-SQL
- Using SQL Server Management Studio
How to Create User in SQL Server Management Studio
Here is a step by step process on how to create a user in SQL Server Management Studio:
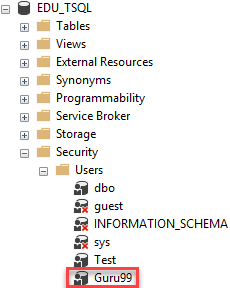
You will be creating a user for the EDU_TSQL database.
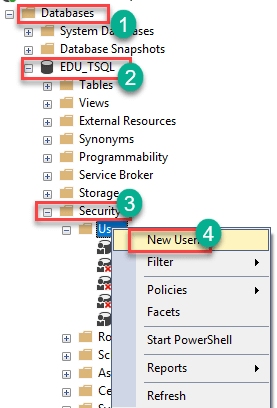
Step 1) Connect to SQL server to create new user
- Connect to SQL Server then expand the Databases folder from the Object Explorer.
- Identify the database for which you need to create the user and expand it.
- Expand its Security folder.
- Right-click the Users folder then choose “New User…”
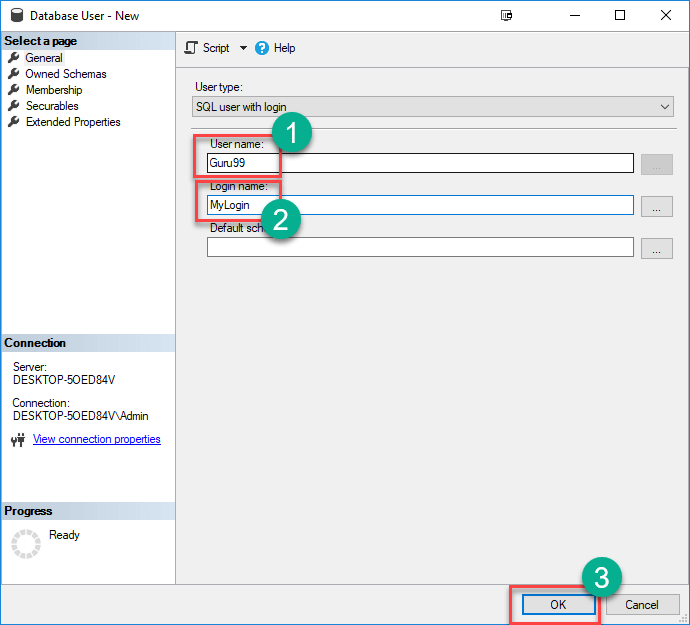
Step 2) Enter User details
You will get the following screen,
- Enter desired User name
- Enter the Login name (created earlier)
- Click OK
Step 3) User will be created
User is created
Create User using T-SQL
You can use the T-SQL’s create user command for SQL server add user to database. The SQL create user command takes the following syntax:
create user <user-name> for login <login-name>
create user Guru99 for login MyLogin
Note: That the query should be executed within the query window. If a user is already created for a Login, SQL Server will throw an error if you create a user for the same login.
Assigning Permission to a User in SQL Server
Permissions refer to the rules that govern the levels of access that users have on the secured SQL Server resources. SQL Server allows you to grant, revoke and deny such permissions. There are two ways to give SQL server user permissions:
- Using T-SQL
- Using SQL Server Management Studio
Assigning Permissions in SQL Server Management Studio
Here is a step by step process on how to assign permissions to a user in SQL server management studio:
Step 1) Connect to your SQL Server instance and expand the folders from the Object Explorer as shown below. Right click on the name of the user, that is, Guru99 then choose Properties.
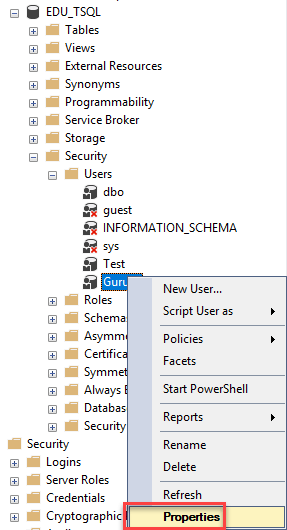
Step 2) In the next screen,
- Click the Securables option from the left.
- Click on Search

Step 3) In the next window,
- Select “All Objects belonging to the Schema.”
- Select Schema name as “dbo”
- Click OK

Step 4)
- Identify Table you want to Grant Permission
- In Explicit Permission select Grant
- Click Okay

Step 5) The user Guru99 is granted SELECT permission on table Course.
Grant Permissions using T-SQL
To grant permission to a user using T-SQL, you first select the database using the use statement. You then assign the permission to the user using the grant statement. Here is the syntax for SQL server create user and grant permission:
use <database-name> grant <permission-name> on <object-name> to <username\principle>
For example, the following command shows how you can grant the select permission to the user Guru99 on the object (table) named Course within the Database EDU_TSQL:
USE EDU_TSQL GO Grant select on Course to Guru99
The permission will be granted!
Granting minimum permissions for data collection
 Apart from the default public role, you can assign the sysadmin role to a user or grant the minimum permissions to a user so that the agent can collect data for data sets.
Apart from the default public role, you can assign the sysadmin role to a user or grant the minimum permissions to a user so that the agent can collect data for data sets.
About this task
You can grant the permissions via user interface or the utility tool permissions.cmd.
Procedure
- To grant the minimum permissions to the user via the user interface, complete these steps:
- Open the Server Roles page and verify that the public check box is selected.
- Open the User Mapping page and then select following checkbox for master database.
- public
- db_owner
- Additionally, on the User Mapping page, select the following check boxes for all the system databases and the user-defined databases which you want to monitor:
- public
- db_ownerFor the msdb database, select the following additional check boxes:
- public
- db_owner
- db_datareader
- SQLAgentReaderRole
- SQLAgentUserRole
- Open the Securables page, and then select the following check boxes for the server instance that you are monitoring:
- view any definition
- view server state
- control server
- To grant the minimum permissions to the user by using the utility tool permissions.cmd, complete the following:
- Launch the Windows Explorer and browse to the utility tool directory Agent_grant_perm_dir:
- For 64-bits agent, Agent_grant_perm_dir is Agent_home\TMAITM6_x64\scripts\KOQ\GrantPermission.
- For 32-bits agent, Agent_grant_perm_dir is Agent_home\TMAITM6\scripts\KOQ\GrantPermission.
- Agent_home is the agent installation directory.Attention: The utility tool permissions.cmd grants db_owner on all databases by default. To exclude certain databases, you must add the database names in the Agent_grant_perm_dir\exclude_database.txt file. The database names must be separated by the symbol alias @.Tip: For example, you want to exclude the databases MyDatabase1 and MyDatabase2, add the following entry in the exclude_database.txt file:
MyDatabase1@MyDatabase2
- Double click permissions.cmd to launch the utility tool.
- Enter the intended parameter values when prompted:Table 1. ParametersParametersDescriptionSQL Server name or SQL Server instance nameEnter the target SQL Server name or the target SQL Server instance name that you want to grant permissions to the user.The existing SQL Server user’s logon nameEnter the user name whose permissions will be altered.Permissions options:
- Launch the Windows Explorer and browse to the utility tool directory Agent_grant_perm_dir:
- 1 Grant db_owner permission
- 2 Grant db_datareader, SQLAgentReaderRole and SQLAgentUserRole permissions
- 3 Grant all required permissions
Source :
- https://www.guru99.com/sql-server-create-user.html
- https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/capmp/8.1.4?topic=monitoring-creating-user-granting-permissions